Global Robotic Mower Industry

Overview of Robotic Lawn Mowers
A robotic lawn mower is an autonomous machine that operates within a defined area to maintain a lawn. The global robotic lawn mower market size was valued at USD 1.5 billion (EUR 1.36 billion) in 2021 and is expected to reach USD 3.9 billion (EUR 3.56 billion) by 2027, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12%.1
Market Dynamics
Regional Dominance: Western Europe's consumer segment currently dominates the robotic mower market. The region's growth prospects are expanding as customers transition from traditional gasoline-powered manual lawnmowers to newer, silent, efficient, smart, and battery-powered robotic mowers.
Commercial Demand: Regular replacement cycles, aging and expanding infrastructure, and a resurgence in golf are driving the demand for commercial lawn mowing equipment. Increased engagement in golf, driven by pandemic trends and a more favourable public outlook, has also contributed to market growth. US golf rounds played increased by 5.5% in 2021, following a 13.9% growth in 2020.2

Beginning Golfers in The U.S. Who Played Their First Ever Round of Golf on a Golf Course
In Millions (1986-Today)
Source: NGC4 2022
Professional Lawn Care Market: The total market value for professional lawn care is estimated at EUR 8.8 billion, with the majority of costs currently attributed to labour operating the mowers. There is significant untapped potential in automating professional lawn mowing tasks.3
Technological Advancements
Major industry players are enhancing their products with features such as ledge sensors, laser vision, lawn mapping, smart navigation, and self-emptying capabilities to improve efficiency.
Robotic Mowing in Golf Courses
Maintenance Costs: Golf courses typically spend around EUR 730,000 annually on maintenance, with labor costs accounting for 50 to 60 percent of the expenses. Fertilizer, equipment, and fuel expenses also contribute to the overall cost.6

Source: GOLF.com7 2020
Labor Shortages: Widespread labor shortages, due to low hourly wages at golf facilities, lead to clubs requiring assistant pros, head pros, or club managers to perform tasks like driving the range-picker instead of more important jobs such as divot-fixing, irrigation, tee maintenance, and repairs. Robotic mowers can alleviate these labor challenges.

Source: GCSAA and Bureau of Labour Statistics8 2016
Technological Benefits: Advancements in battery-powered robotic and autonomous mowers allow facilities to reduce labor budgets and energy expenses without compromising playing conditions.
Research and Field Trials: Research conducted by an Italian group on semi-rough and fairway turfgrass showed that robotic mowers provided better turfgrass quality, higher tiller density, and finer turfgrass leaves compared to manual rotary mowers and manual triplex cylinder (reel) mowers. Preliminary results from field trials at the NIBIO Turfgrass Research Center Landvik, Norway, and demonstration trials in five Nordic countries indicated that turfgrass quality with robotic mowing was similar to manual mowing.
Player Attitudes: A survey of players' attitudes towards robotic mowers on five golf courses revealed that about 90% of the players were positive or neutral towards the new technology.
|
Trading Comparables (In USD million, as on May 8, 2023) |
|
||||||
|
Company |
Enterprise Value (EV) 5 |
Revenue (TTM) |
EBITDA (TTM) 6 |
EV / Revenue |
EV / EBITDA |
|
|
|
Husqvarna AB 1 |
6,383 |
5,088 |
454 |
1.3x |
14.0x |
||
|
Stanley Black & Decker, Inc. 2 |
20,370 |
16,947 |
949 |
1.2x |
21.5x |
||
|
Deere & Company 5 |
1,62,470 |
54,937 |
13,684 |
3.0x |
11.9x |
||
|
Median |
|
|
|
1.3x |
14.0x |
||
|
Transaction Comparables (in USD million, as on May 8, 2023) |
|||||||
|
Target |
Acquirer |
Target Description |
EV |
EV/ Revenue |
EV/ EBITDA |
||
|
MTD Holdings Inc 4 |
Stanley Black & Decker |
MTD designs, manufactures and distributes lawn tractors, zero turn mowers, walk behind mowers, snow blowers, residential robotic mowers, handheld outdoor power equipment and garden tools for both residential and professional consumers under well-known brands like Cub Cadet® and Troy-Bilt®. MTD has state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities in North America and Europe, and a global distribution network. |
2,000 |
0.8x |
8.0x |
||
|
Combined Median |
|
|
|
1.2x |
13.0x |
||
Porter's Five Forces
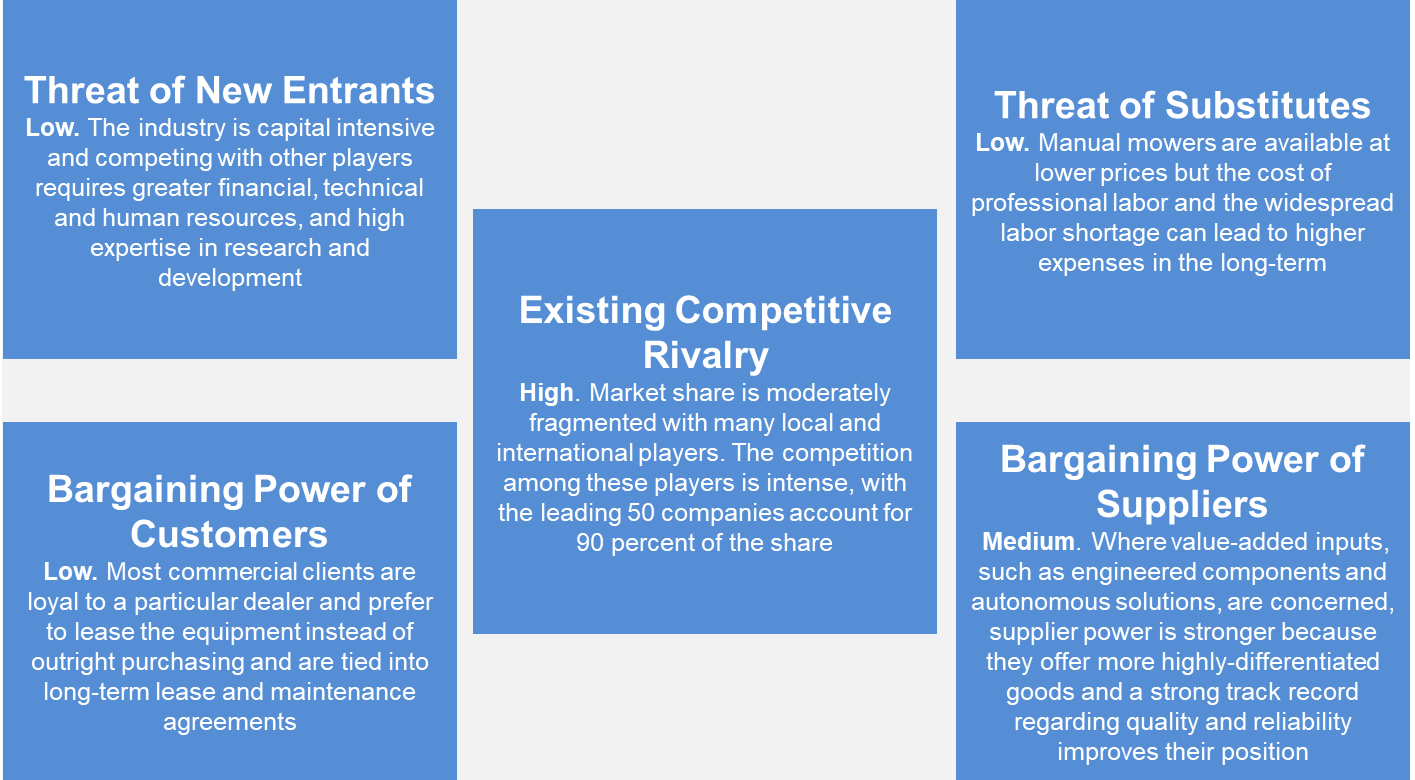
Threat of New Entrants - Low
The industry is capital intensive and competing with other players requires greater financial, technical and human resources, and high expertise in research and development.
Existing Competitive Rivalry - High
Market share is moderately fragmented with many local and international players. The competition among these players is intense, with the leading 50 companies accounting for 90 percent of the share.
Threat of Substitutes - Low
Manual mowers are available at lower prices but the cost of professional labor and the widespread labor shortage can lead to higher expenses in the long-term.
Bargaining Power of Customers - Low
Most commercial clients are loyal to a particular dealer and prefer to lease the equipment instead of outright purchasing and are tied into long-term lease and maintenance agreements.
Bargaining Power of Suppliers - Medium
Where value-added inputs, such as engineered components and autonomous solutions, are concerned, supplier power is stronger because they offer more highly-differentiated goods and a strong track record regarding quality and reliability improves their position.